Figure 1 gives an example of a course for a street race. You see some points, labeled from 0 to N (here, N=9), and some arrows connecting them. Point 0 is the start of the race; point N is the finish. The arrows represent one-way streets. The participants of the race move from point to point via the streets, in the direction of the arrows only. At each point, a participant may choose any outgoing arrow.
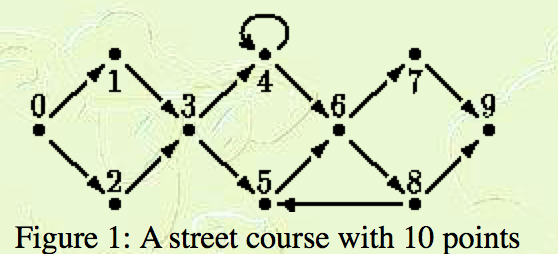
Figure 1: A street course with 10 points
A well-formed course has the following properties:
- Every point in the course can be reached from the start.
- The finish can be reached from each point in the course.
- The finish has no outgoing arrows.
A participant does not have to visit every point of the course to reach the finish. Some points, however, are unavoidable. In the example, these are points 0, 3, 6, and 9. Given a well-formed course, your program must determine the set of unavoidable points that all participants have to visit, excluding start and finish.
Suppose the race has to be held on two consecutive days. For that purpose the course has to be split into two courses, one for each day. On the first day, the start is at point 0 and the finish at some `splitting point'. On the second day, the start is at this splitting point and the finish is at point N. Given a well-formed course, your program must also determine the set of splitting points. A point S is a splitting point for the well-formed course C if S differs from the star t and the finish of C, and the course can be split into two well-formed courses that (1) have no common arrows and (2) have S as their only common point, with S appearing as the finish of one and the start of the other. In the example, only point 3 is a splitting point.